If you are not between the ages of 6 and 13, having a loose tooth is a big deal. No matter what’s wrong, the first thing you should do is make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible. In this article, we’ll talk about the different things that can cause loose teeth, the treatment that’s needed, and the long-term effects.
Loose permanent teeth can be caused by two different things. Some are caused by injuries, and others are caused by the damage that dental disease does.
Injuries that Loosen a Tooth or Teeth
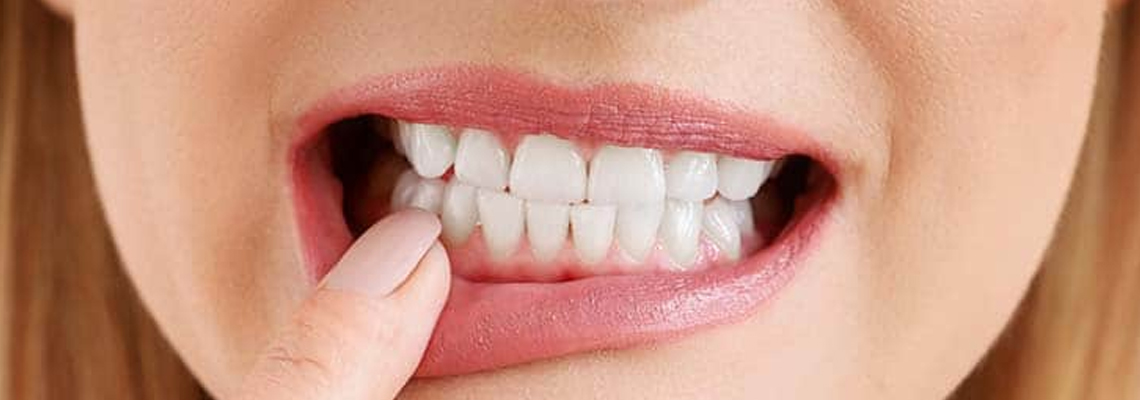
When someone gets hurt in the face or mouth, their teeth can come loose. This kind of injury can also cause teeth to chip, tooth roots to break, or the jawbone to crack. If the injury doesn’t break the tooth or bone, it’s likely to loosen the tooth.
A ligament called the periodontal ligament connects each tooth to the bone around it. Like any other part of the body, a heavy force can stretch or tear this ligament. A mouth injury can not only stretch or tear this ligament, but it can also change the shape of the bone. The jawbone is soft and can be pushed in, especially where the upper teeth are. If you get hurt and put pressure on a tooth, the bone socket that holds it can get bigger.
Dental Disease that Loosens a Tooth or Teeth
When a tooth is loose because of dental disease, it is not because the tissues around the tooth are getting bigger or stretching. It causes those tissues to break down. This can happen if the gum disease or tooth infection is very bad.
The bacteria in dental plaque are what cause gum disease to start. Around a tooth or teeth, these bacteria gather and make poisons. The toxins get into the gums and make the body react with inflammation. If the inflammation isn’t taken care of, it slowly destroys the ligaments, jawbone, and gums around the diseased area. As the tooth loses its hold on the hard tissue around it, it can start to come loose. A good example of this in nature is a plant that has the ground around it worn away. At some point, there won’t be much holding the plant in place, and it will fall over or tip. Before the tooth falls out completely, it comes loose in the mouth.
In a dental infection caused by an abscessed tooth, the toxins from the bacteria cause the same thing to happen at the end of the tooth’s root. As the bone slowly wears away, the tooth can actually loosen from the “bottom” up. Fewer people have this than gum disease. As the infection presses on the end of the root, it can make a tooth look “longer” than the teeth next to it. Most of the time, you can push the tooth back into place by pressing on it from the side.
How does a dentist fix a tooth that is loose?
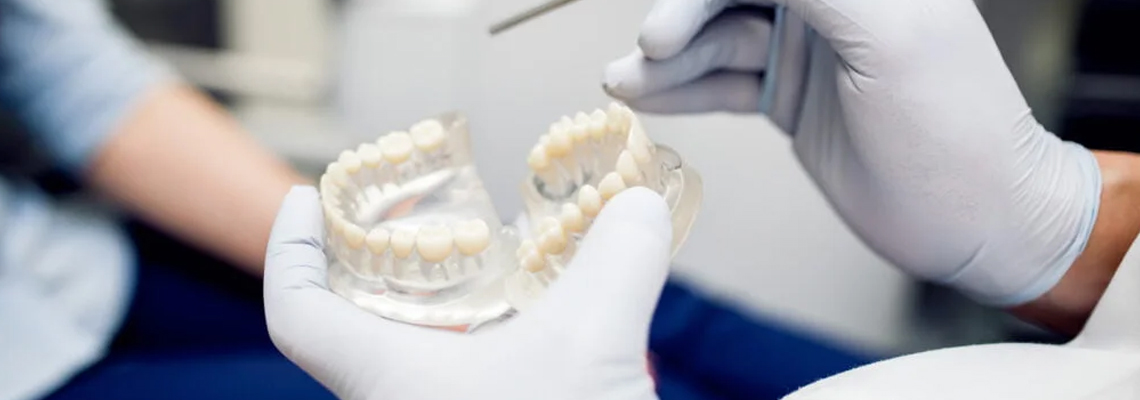
The best way to treat a problem is to figure out what it is. Your dentist will use either close-up x-rays or three-dimensional imaging to check the health of the tooth and all of the tissues around it. This has to be done to rule out any broken teeth or jawbones. It is also an important part of figuring out what’s wrong with your teeth.
When a tooth is hurt, it needs to be stabilized so that the body can heal the tissues around it. This could mean wearing a mouthpiece or having a piece of wire bonded across several teeth to hold them in place. It always involves taking pressure off the teeth that are hurting, so you will need to follow your dentist’s instructions as closely as you can. We know that no one wants to eat only liquids, but we also know that this is the best way for you to get better.
When gum disease is the cause of loose teeth, your dentist must figure out what the long-term effects of periodontal treatment will be. Sometimes, the tooth can’t be saved because too much bone has been lost. If periodontal treatment doesn’t work or can’t help, your dentist will pull out the loose tooth or teeth. If you treat the gums and are able to get the tissues around the affected teeth to grow back together, you might be able to save them.
When a loose tooth is caused by a dental abscess from a large cavity or crack, the tissues around the tooth usually heal well once the source of the infection has been completely treated. Most of the time, this means getting a root canal to get rid of the infected tissue inside the tooth. Once we stop the bacteria from making poisons, the bone and ligament around the tooth will heal and join back together.
What are the Long-Term Consequences of a Loose Tooth?
Even after a loose tooth has been fixed and healed, it may still be at risk for other problems in the future. When a sharp force hurts a tooth and the tissues around it, the nerve inside could die. Some people with teeth that have gotten back to normal will need root canals on the hurt teeth years after the accident.
People who had a dental disease that caused their teeth to loosen and were treated for it are still at risk of getting those infections again. Patients with gum disease must take care of their teeth for the rest of their lives to keep the disease from coming back and doing more damage. Root canal-treated teeth can get infected again, which means they need more care.
The most important thing to know is that your dentist will need to check on any loose teeth for a long time. When you go to the dentist regularly, she will keep a close eye on your teeth for signs of problems that keep coming back. No matter what caused the looseness, you need to keep an eye out for more problems. The best chance of success is when help is given early on.
Got More Questions?
Call our office right away to set up an appointment with Dr. Motiwala. He can answer your specific questions, figure out what’s wrong, and talk to you about how to treat it.
Are You Looking For Dental Implants
Click on the links below to learn more about the approximately $50,000 savings option for Dr. Motiwala’s packages.
- Full mouth dental implants & Cost of Treatment
- Smile Makeover & Cost of Treatment
- Watch 100’s of Testimonials from our International Patients
Make An Appointment!
Please contact us if you have dental difficulties or are interested to know about dental implants and how they might improve your smile. Dr. Motiwala Dental Clinic & Implant Center may be reached at +91 99596 14584. You can also Contact Us by clicking the banner below.